PRODUCTS & PROJECTS
KATHIRON CONTROL SYSTEM
( industrial electrical & automation Solution provider )
PRODUCTS AND SOLUTION
Motor Control Center ( IMCC / MCC )
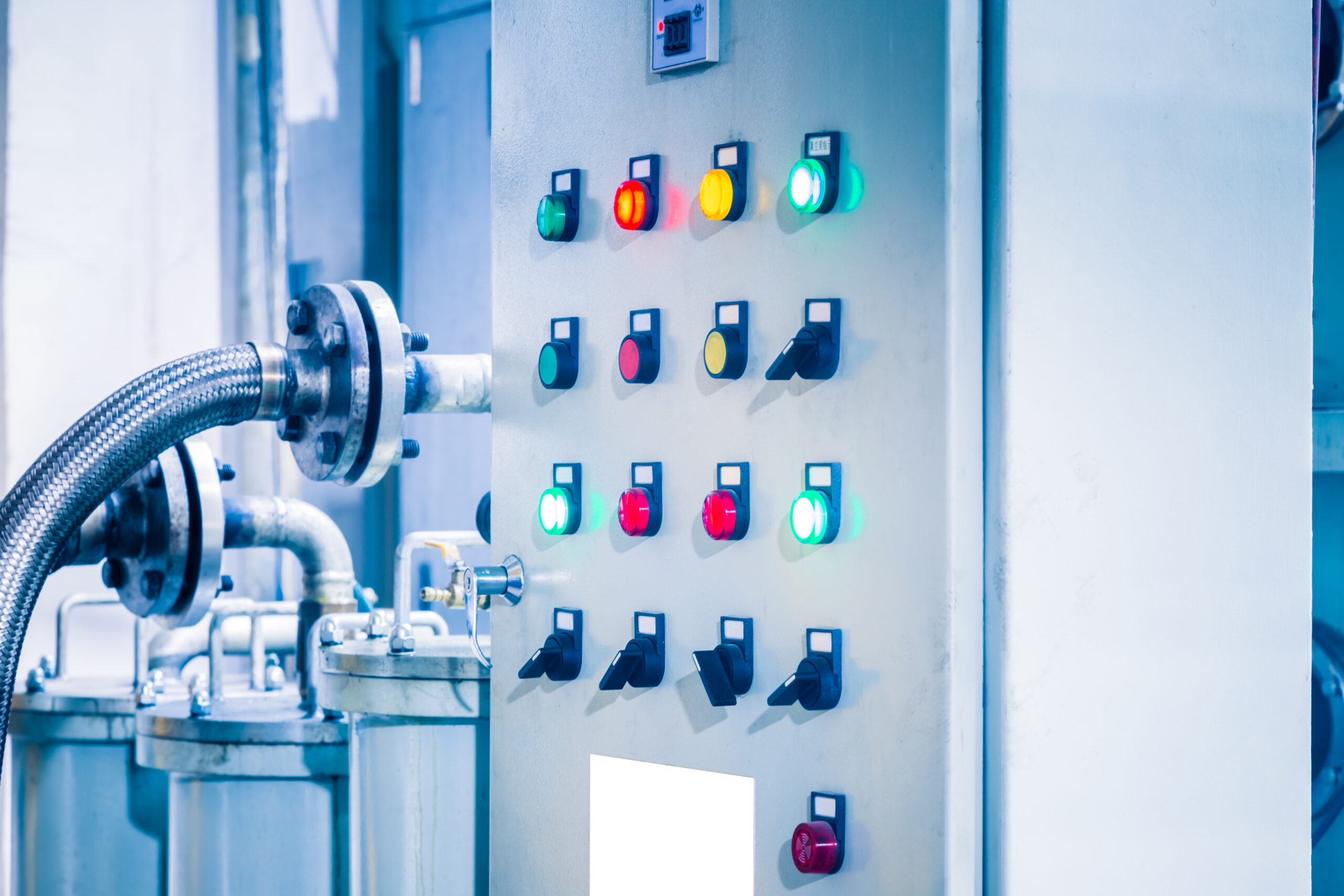

Motor Control Center ( IMCC/MCC)
An Intelligent Motor Control Center (IMCC) is an advanced version of a traditional Motor Control Center (MCC), integrated with sophisticated monitoring, control, and communication capabilities. IMCCs are designed to manage and protect electrical motors in industrial applications more efficiently by incorporating digital technologies, advanced diagnostic tools, and real-time data analysis. A Motor Control Center (MCC) is a centralized system used to control and protect electrical motors in industrial applications. It houses electrical components such as circuit breakers, fuses, starters, and relays, which are used to manage motor operation, monitor performance, and ensure safety. MCCs are commonly found in industries like manufacturing, water treatment, HVAC, and power generation.
Applications of Motor Control Centers (IMCC / MCC):
- Food and Beverage: Motor control in mixing, pumping, and packaging processes.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Efficient control of pumps, blowers, and other motor driven equipment in treatment plants.
- Mining and Minerals Processing: Control of motors in crushers, conveyors, and mills.
- Manufacturing: Control of motors in production lines, conveyors, mixers, and other machinery.
- Oil and Gas: Motor control for pumps, compressors, and other critical systems in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations
- Power Generation: Control of motors driving various generators, compressors, and auxiliaries in power plants.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring precise and reliable operation of motors used in production, mixing, and packaging.
- HVAC Systems: Managing motors for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning in commercial or industrial buildings.
Frequency Drives
Variable Frequency Drives
VFDs are commonly used to regulate the operation of motors in various industrial applications, including pumps, fans, conveyors, HVAC systems, and more.
Advantages :
Reduced Energy Consumption: Adjusts motor speed to match load requirements in pumps, fans, and compressors, cutting unnecessary power use.
Extended Equipment Life: Soft start/stop minimizes mechanical stress, reducing wear on motors and components.
Enhanced Process Control: Enables precise speed regulation for more stable and accurate operations.
Lower Mechanical Stress: Controlled acceleration and deceleration prevent damage from sudden starts and stops.
Quieter Operation: Reduced speeds lead to less noise, especially in fan and pump applications.
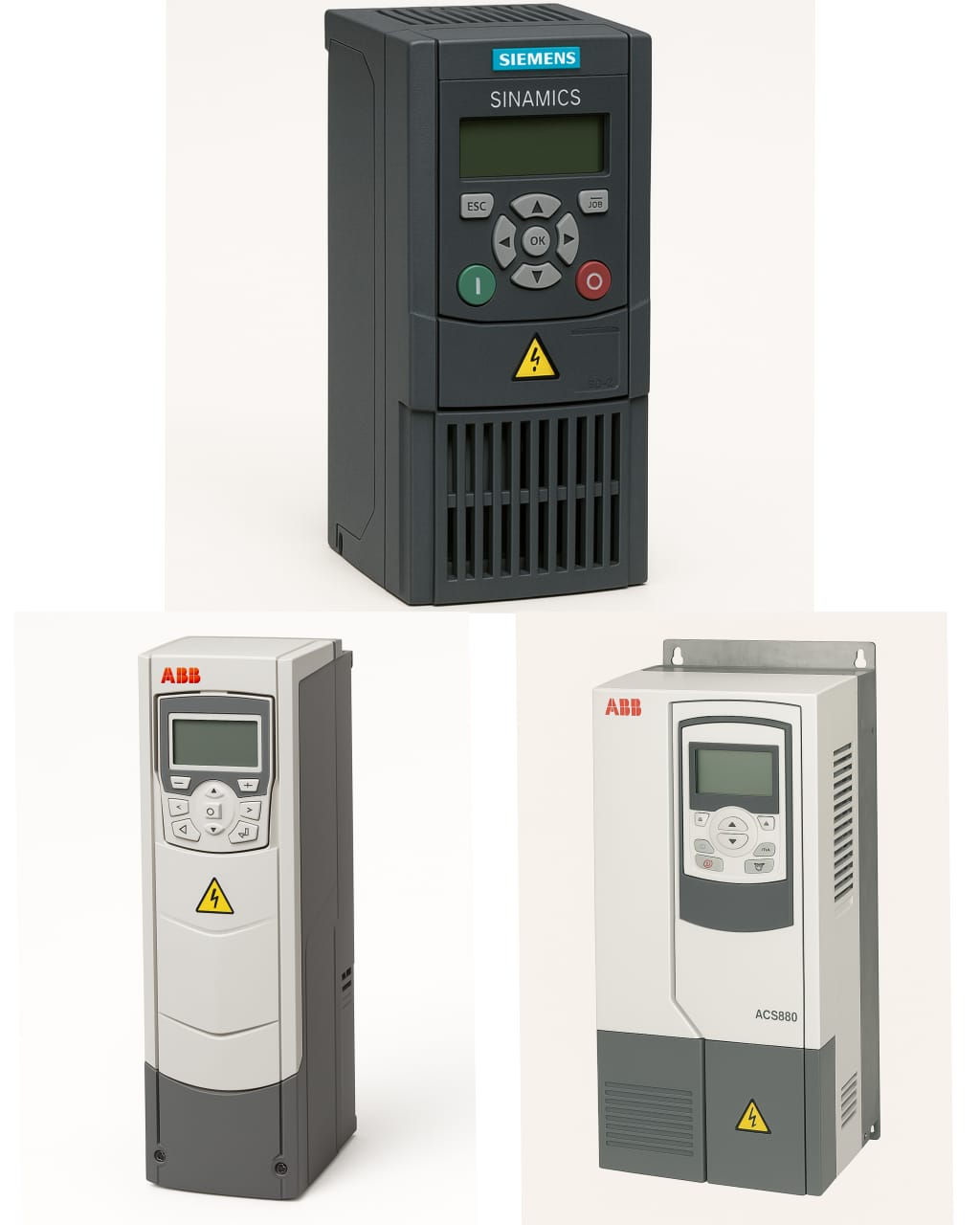

Applications of VFDs:
- Fans and Blowers: industrial settings, VFDs can adjust the speed of fans and blowers to meet varying airflow requirements.
- Pumps: VFDs are often used in pumping systems to adjust the flow rate. By controlling the speed of the motor, a VFD can match the flow with demand, leading to energy savings and more precise control.
- Conveyors: On conveyor belts, VFDs can control the speed and direction of the motor, allowing for smooth operation and efficient material handling.
- Compressors: VFDs in compressors help maintain the required pressure levels without wasting energy, as they can adjust the motor speed to match the load.
- Mills: Mills can process large volumes of materials at high speeds, enabling large-scale production.
- Centrifuges and Mixers: In applications that require varying speed or torque, such as in centrifuges and mixers, VFDs offer better control and precision.
- HVAC Systems: VFDs are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to control the speed of fans and pumps. This helps maintain desired environmental conditions efficiently and reduces power consumption.
Energy Management System

Energy Management System
A framework of tools and processes that track, control, and optimize energy use in organizations, buildings, or industrial facilities, aiming to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and promote sustainability.Its primary goal is to improve energy efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure sustainability by tracking energy consumption and identifying opportunities for energy-saving measures.
Applications of Energy Management System:
- Cost Reduction: Lower energy consumption leads to reduced utility bills.
- Sustainability: Helps reduce carbon emissions and supports corporate sustainability initiatives.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: By streamlining energy use, facilities can improve their overall operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Facilitates compliance with government and industry regulations regarding energy use and emissions
- Data-Driven Decisions: Provides accurate data for better decision-making and the development of energy-saving projects.
Motor & Drive System
SERVO MOTOR & DRIVES SYSTEMS
Servo Motor :
A servo motor is a special type of motor designed for precise control of angular position, speed, and torque. Unlike standard motors, which simply run at a fixed speed when powered, a servo motor can be precisely controlled and positioned based on feedback from sensors, making them ideal for systems that require high accuracy

Drives System:
A servo drive (or servo amplifier) is an electronic device that controls the performance of a servo motor. It provides the necessary power to the motor and receives feedback from the motor’s encoder or resolver to adjust speed, position, and torque in real-time. The drive acts as the interface between the controller (e.g., PLC, motion controller, or CNC) and the motor.
Process Instruments

PROCESS INSTURMENTS
Process Instrumentation refers to the collection of instruments, sensors, and control systems used to monitor and control industrial processes. It plays a vital role in ensuring that operations run efficiently, safely, and within required specifications. These systems are critical in industries such as oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, power generation, pharmaceuticals, and foodprocessing
Applications of Process Instrumentation:
- Food and Beverage: Controlling processes like pasteurization, fermentation, and packaging while maintaining hygiene standards and product quality.
- Water Treatment: Monitoring and controlling flow, level, pressure, and chemical dosing in water treatment plants to ensure safe water delivery
- Power Generation: turbine performance, boiler pressure, temperature, and fuel flow in power plants for optimal performance and safety.
- Oil and Gas: Monitoring and controlling pressure, temperature, flow, and composition in pipelines, refining, and drilling processes.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Controlling chemical reactions, managing pressure, temperature, flow, and ensuring safety in plant operations.
- Pharmaceutical: Ensuring precise control of environmental conditions, pH, temperature, and humidity in drug manufacturing processes.
Power Control Center
POWER CONTROL CENTER
A Power Control Center (PCC) is a centralized facility or system used to monitor, control, and manage the generation, distribution, and consumption of electrical power within a grid or a specific power system. The Power Control Center plays a vital role in ensuring the reliability, stability, and efficiency of power generation and distribution networks, typically in large-scale utilities, industrial plants, or power distribution systems.


Applications of Power Control Centers:
- Distribute electrical power to lighting, HVAC systems, and office equipment.
- Control and distribute power to pumps, aeration systems, and treatment units.
- Control and monitor power usage across automated processes.
- Distribute power to mining equipment like crushers, conveyors, and drills.
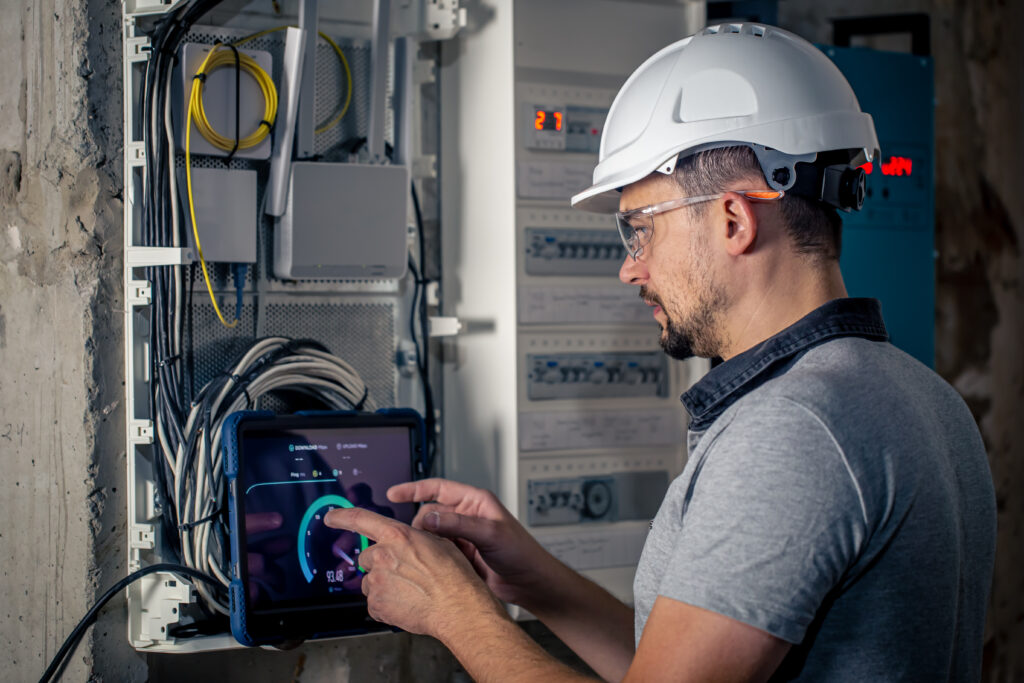
Human Machine Interface
HUMAN MACHINE INTERFACE
HMI stands for Human-Machine Interface, which refers to the interaction between a human and a machine, system, or device. It is a critical component in various fields, particularly in industrial, automotive, and technology sectors. An HMI allows users to control and monitor systems, usually by providing visual displays, touchscreens, or physical buttons.
Key Aspects of HMI:
- User Interface (UI): visual and interactive part where users can view system status, adjust settings, or control the system.
- Control Mechanism: This can include buttons, touchpads, dials, or even voice commands that allow users to control the machine.
- Data Visualization: HMIs often present data in graphical formats, such as charts, gauges, or numerical readings, to help users make decisions or monitor processes.
- Feedback: Provides real-time feedback to users about the system’s operation, often in the form of alarms, warnings, or status indicators

Types of HMIs:
- Basic HMI: Often just a simple interface with buttons or a small display
- Advanced HMI: Incorporates touchscreens, complex graphics, and multimedia features
- Embedded HMI: A more compact, integrated system, often found in devices like microwaves, washing machines, or vending machines.
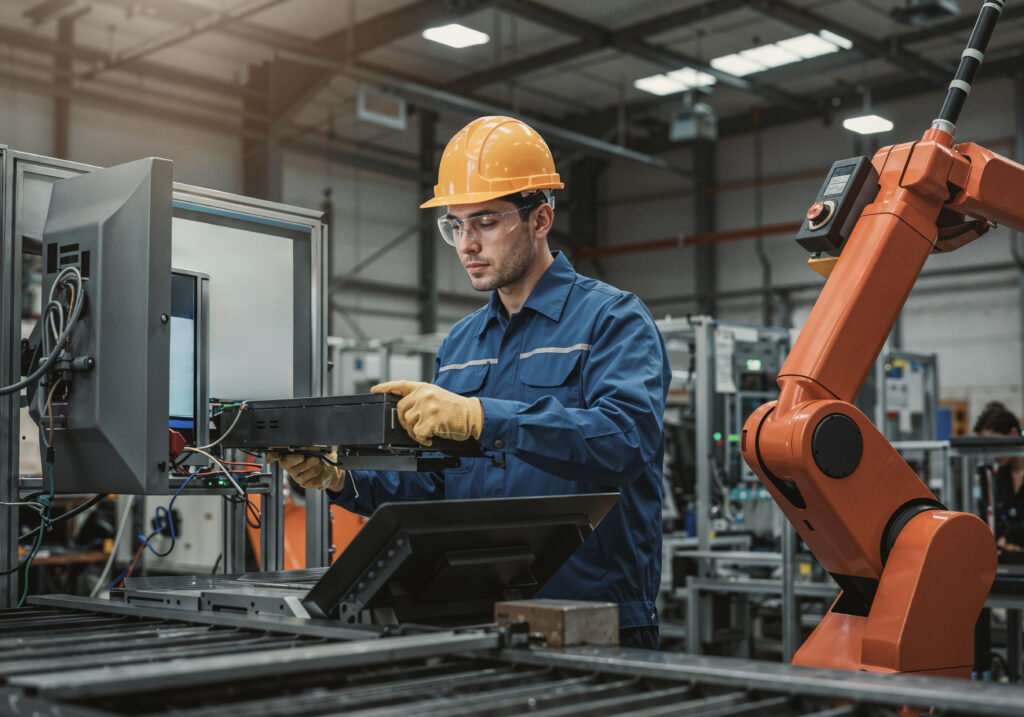
Programmable Logic Controllers
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an industrial digital computer used to control manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, robotic devices, or other activities that require high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis


Applications:
- Automation in Manufacturing: Controls machines, assembly lines, and processes.
- Energy Management: Controls systems for efficient energy use.
- Building Automation: Manages HVAC, lighting, and security systems.
- Infrastructure: Used in water treatment plants, transportation systems, etc
